What Is the Overall Frequency Range of 5G?
The deployment of 5G technology marks a significant advancement in the field of wireless communications, offering faster speeds, greater capacity, and lower latency compared to its predecessors. A critical aspect of this technology lies in its diverse frequency spectrum, which is specifically designed to accommodate a wide array of applications and services. Understanding the overall frequency range of 5G is key to grasping how this technology can achieve such remarkable performance and versatility.
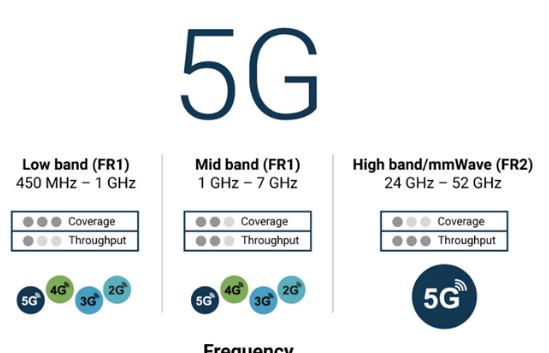
Broad Spectrum Coverage
5G technology utilizes a comprehensive range of frequencies, divided into three main categories: low-band, mid-band, and high-band. Each band plays a pivotal role in ensuring that 5G networks can provide extensive coverage, high-speed data transmission, and penetrate urban, suburban, and rural areas effectively.
Low-Band Spectrum
The low-band part of the 5G spectrum generally includes frequencies below 1 GHz. These frequencies are renowned for their ability to cover vast distances and penetrate obstacles like buildings and trees effectively. This makes them ideal for providing broad coverage, especially in rural areas where higher frequencies may not reach. Common low-band frequencies used in 5G include:
- 600 MHz
- 700 MHz
- 800 MHz
These bands are crucial for carriers looking to offer nationwide coverage and improve indoor network performance.
Mid-Band Spectrum
Mid-band frequencies, ranging from 1 GHz to 6 GHz, offer a balanced mix of coverage and capacity. This spectrum is particularly valuable in urban and suburban areas, providing faster speeds and lower latency than low-band without the range limitations of high-band frequencies. Key mid-band frequencies utilized in 5G include:
- 2.5 GHz
- 3.5 GHz
- 3.7 GHz
This range is the workhorse for most 5G deployments, providing the bulk of 5G's speed and capacity improvements over 4G LTE.
High-Band Spectrum (Millimeter Wave)
At the upper end of the 5G spectrum, high-band frequencies, or millimeter waves, cover frequencies from 24 GHz to as high as 52.6 GHz. These frequencies can deliver ultra-high speeds and massive capacity, which are essential for bandwidth-intensive applications such as virtual reality, ultra-HD video streaming, and advanced industrial applications. However, they come with limitations in coverage and building penetration, requiring a dense network of antennas. Notable high-band frequencies include:
- 28 GHz
- 39 GHz
- 47 GHz
These are typically used in densely populated urban areas to provide enormous data capacity where it is most needed.
Strategic Importance of 5G's Frequency Diversity
The diverse frequency range of 5G allows for tailored network configurations that meet specific needs—from widespread coverage in rural areas using low-band frequencies to high-capacity, high-speed requirements in urban centers using high-band frequencies. This flexibility is crucial for supporting the wide variety of devices and applications that characterize today's digital landscape, including smartphones, autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and much more.
The effective management and utilization of this broad frequency spectrum are what enable 5G networks to support the next wave of technological innovation, transforming industries and enhancing day-to-day experiences with faster, more reliable wireless service.